HTML + Contentful tutorial
This tutorial teaches the basics of Netlify Create without the need to know any particular framework, using Contentful as the content source.
# Project setup
Let’s begin by getting the example project setup on your local machine.
# Prerequisites
- Machine equipped to run Node.js v14 or newer.
- Contentful account
- Blank Contentful space (without content or content models)
- API access to your Contentful space, including space ID, delivery and preview tokens, and a personal access token (sometimes called a management token)
# Clone example project
Use create-stackbit-app to clone the example project and install dependencies.
npx create-stackbit-app@latest --example tutorial-html-contentful
Change into the project directory when installation has completed. Unless otherwise noted, all commands will be run from the project root.
cd tutorial-html-contentful
# Set environment variables
Copy .env.example to .env and set the appropriate values.
CONTENTFUL_SPACE_ID="..."
CONTENTFUL_DELIVERY_TOKEN="..."
CONTENTFUL_PREVIEW_TOKEN="..."
CONTENTFUL_MANAGEMENT_TOKEN="..."
# Import content
Run the setup script to fill the new space with content models and sample content.
npx cross-env npm run setup
# Run the website
Start the development server and view the site at localhost:3000.
npm run dev

# Netlify Create configuration
Adding Netlify Create's local visual editor application to an existing site takes just a few quick steps.
# Install CLI
Install the Stackbit CLI for Netlify Create, which we'll use to launch the visual editor.
npm install -g @stackbit/cli@latest
# Run visual editor
With the development server still running on port 3000, open a new terminal session to run the visual editor using the CLI's dev command.
stackbit dev
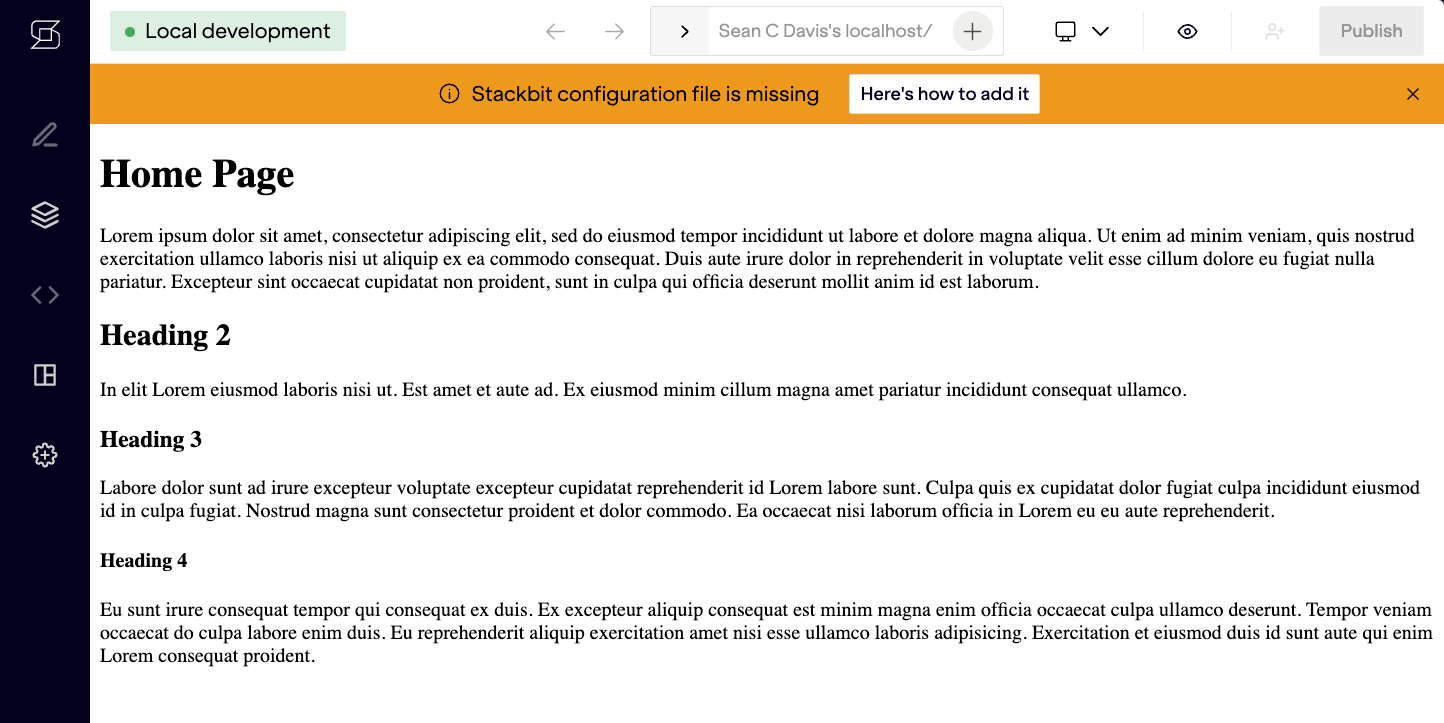
Now, if you visit localhost:8090, you'll see the example project that is running on port 3000. The application running on port 8090 is a local Netlify Create application that proxies to your development server, and also contains a few assets and routes to facilitate visual editing.
# Register your project
One such route is /_stackbit. This will redirect to the authentication process that makes it possible to work with Netlify Create locally.
Open localhost:8090/_stackbit in your browser and create an account. You'll be redirected to a new URL that is unique to your local editing environment. The preview you see here is the application running on localhost:8090.
# Configure content source
Next, we have to add our configuration file to tell Netlify Create how content is stored. First, install a couple development dependencies. (Netlify Create does not require any production dependencies.)
npm install -D @stackbit/cms-contentful @stackbit/types
Then, add a stackbit.config.ts configuration file that specifies the source of content as Contentful. This is the minimum configuration needed to work with this project locally.
// stackbit.config.ts
import { ContentfulContentSource } from "@stackbit/cms-contentful";
import { defineStackbitConfig } from "@stackbit/types";
export default defineStackbitConfig({
stackbitVersion: "~0.6.0",
contentSources: [
new ContentfulContentSource({
spaceId: process.env.CONTENTFUL_SPACE_ID!,
environment: process.env.CONTENTFUL_ENVIRONMENT || "master",
previewToken: process.env.CONTENTFUL_PREVIEW_TOKEN!,
accessToken: process.env.CONTENTFUL_MANAGEMENT_TOKEN!
})
]
});
Note
Netlify Create automatically loads the content from .env into process.env.
# Basic content editing
Notice that the content tab is populated with the content in your Contentful space. This is editable via a two-way content sync.
You can edit in Netlify Create and it will be saved in Contentful. Or you can edit in Contentful, and the new values will be pulled into Netlify Create automatically.
# Page editing
Pages are a type of model that represent a single URL path in your site.
When the proper configuration, Netlify Create can build a complete sitemap and show the proper content fields as editors navigate between pages in the application. This requires specifying which models represent pages and how each page maps to a URL path in the site.
# Specify page models
Open the stackbit.config.ts file and add a modelExtensions property to declare the page model as a page model.
// stackbit.config.ts
import { ContentfulContentSource } from "@stackbit/cms-contentful";
import { defineStackbitConfig } from "@stackbit/types";
export default defineStackbitConfig({
stackbitVersion: "~0.6.0",
contentSources: [
new ContentfulContentSource({
// ...
})
],
modelExtensions: [{ name: "page", type: "page", urlPath: "/{slug}" }]
});
This tells Netlify Create to extend its knowledge about the Contentful model with an ID of page — to declare it with a page type, and to map its URLs paths using the slug field within the page model.
# Sitemap navigator
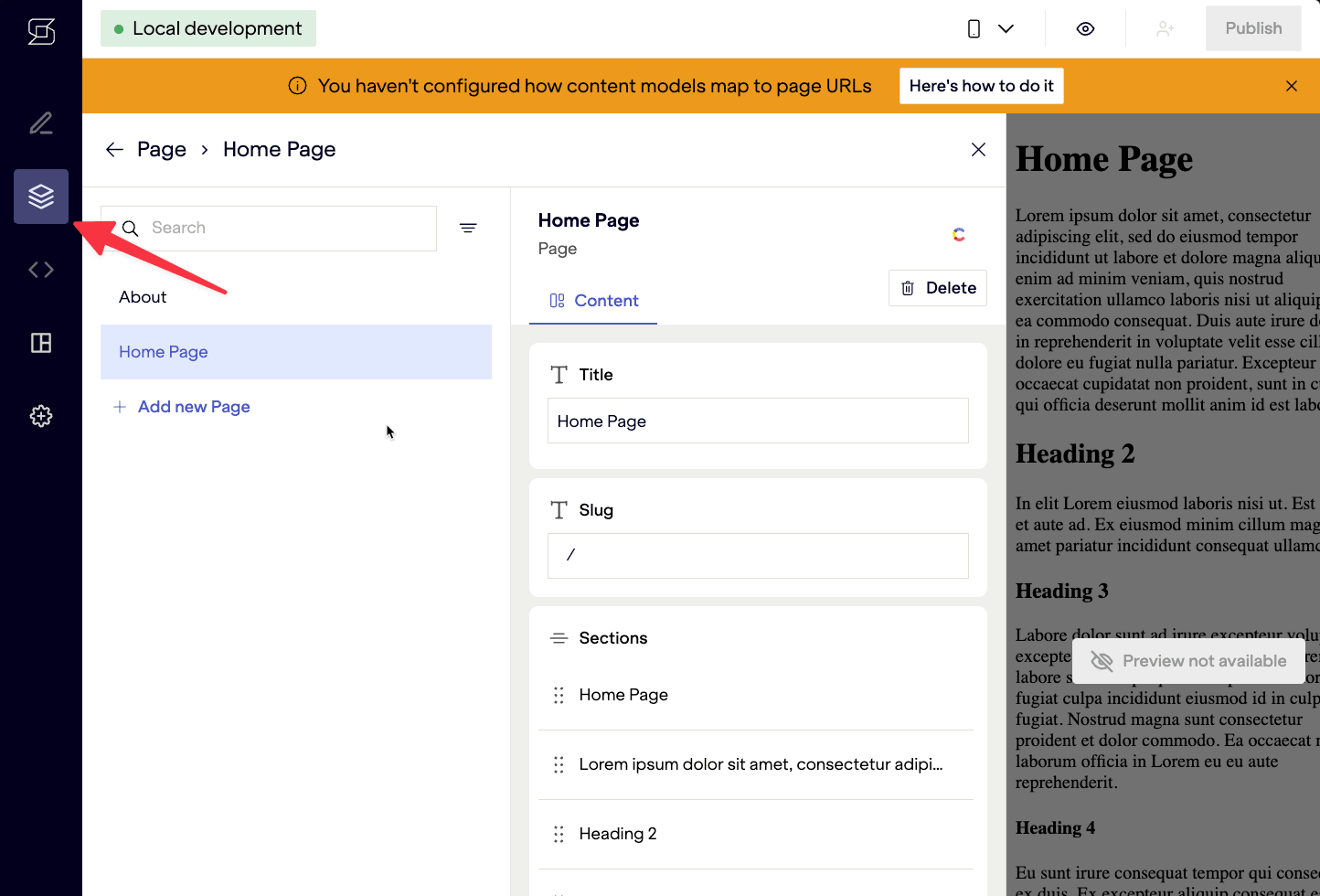
Going back to the Netlify Create editor, you should now see the sitemap populated with the home page entry, which was added to the CMS when importing content.
# Contextual page editor
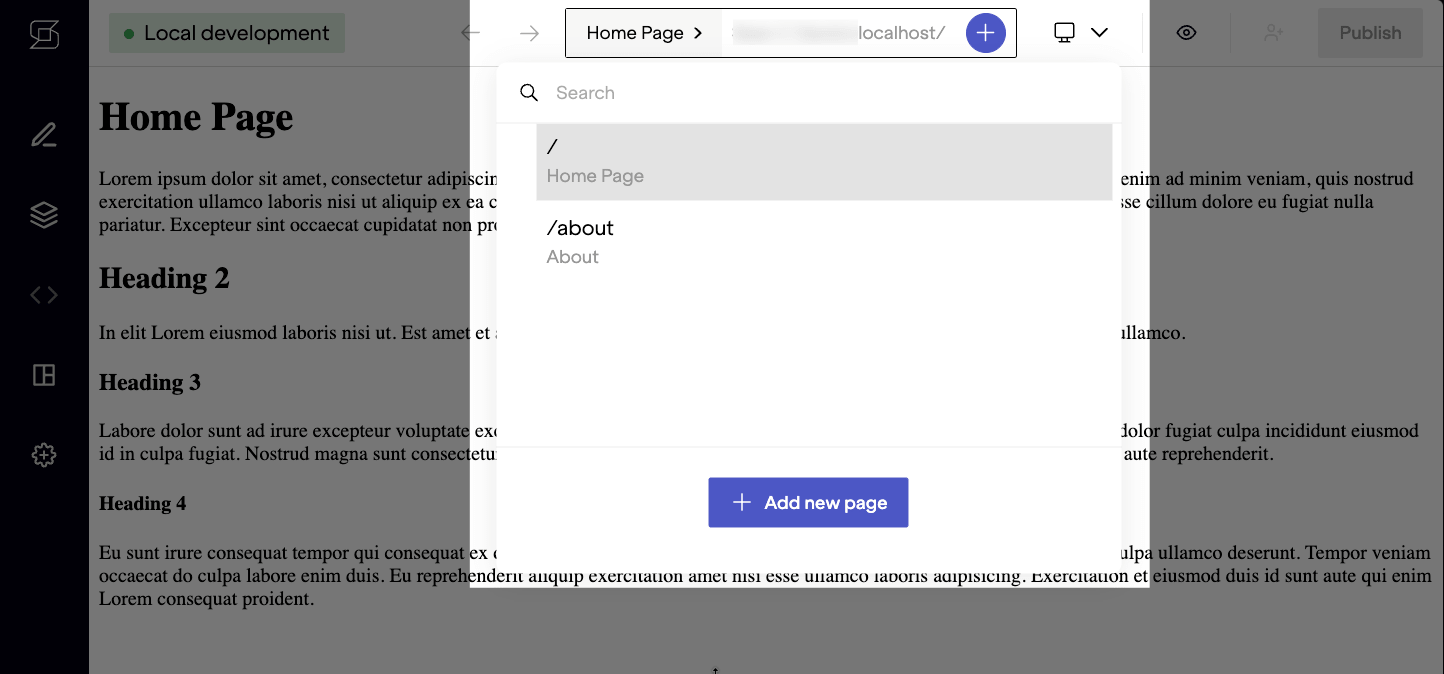
This change also enabled the contextual page editor (pencil icon in left sidebar). Notice that you can open this panel and see the fields and values for this page.

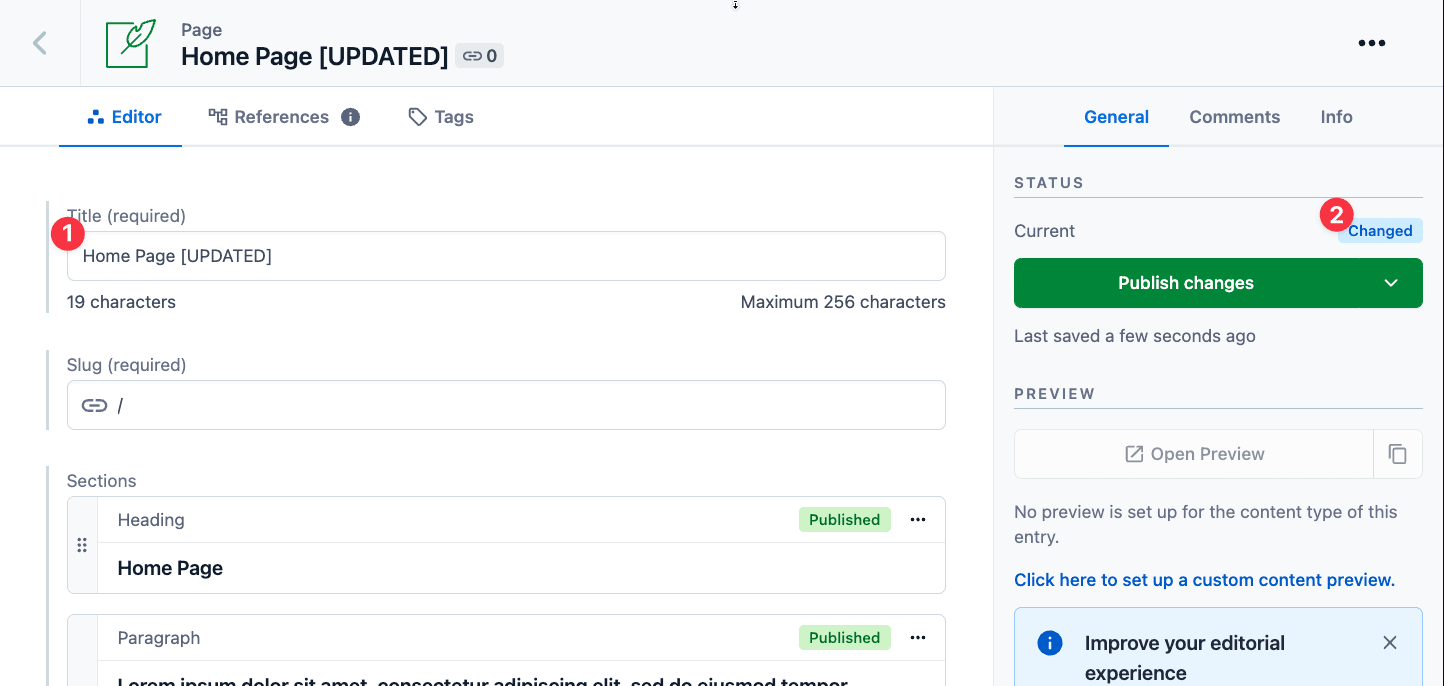
As with basic content editing, making changes here will update content in Contentful in an changed (unpublished) state.
# Inline editing
The most advanced (and productive) form of editing with Netlify Create is inline editing, which is made possible through the use of annotations.
These are simple HTML data attributes (data-sb-object-id and data-sb-field-path) that map content in Contentful to elements on the page. This enables editors to click directly in the preview, make a change, and see that change reflected in Contentful.
Here, we'll make the content field in the paragraph component editable inline.
# Set the object ID
The first step is to declare the ID of the content object using a data-sb-object-id attribute. This points Netlify Create to the origin of the content on the screen.
Note
In Contentful, every entry has an automatically assigned identifier stored in its sys.id property, delivered from the API.
In the tutorial's code, the lib/contentful.js module is tasked with fetching data from Contentful and returning it to lib/framework.js as JavaScript objects. The fetched sys.id value is mapped to an id property in the returned objects.
Add a wrapping <div> to the paragraph component and attach the data-sb-object-id attribute to it to set the object ID context.
<div data-sb-object-id="<%- id %>">
<p><%= content %></p>
</div>
This annotation the children of this wrapping <div> with a particular Contentful entry.
# Add the field path
Now that the component is annotated with the ID of the paragraph content entry, we can use the data-sb-field-path data attribute to make fields within the component editable inline.
<div data-sb-object-id="<%- id %>">
<p data-sb-field-path="content"><%= content %></p>
</div>
Now inline editing will work! You can hover over an element on the page to highlight and change it.

# Additional capabilities
You have now added visual editing to an HTML + Contentful site with Netlify Create! But this is just the beginning. You can expand on what you learned above, or explore additional ways to extend the visual editing experience for your site.
This is typically what developers explore next:
- Create content presets for more productive content editing
- Extend a field type with content modeling
And as you progress, there are more advanced features to consider:
- Localization
- When your ready to onboard your business users, create a cloud project to enable collaboration and publishing
- Control access to content, including managing editorial permissions
Did you find this doc useful?
Your feedback helps us improve our docs.